Types of Queries Picked Up by AI Engines
Discover the main types of queries AI engines pick up, how they differ from traditional search, and what this shift means for your SEO and content strategy. Learn the patterns driving AI first discovery in 2025.
Written by
AI search
Nov 20, 2025
Introduction & Why this matters
If Google showed us what people were curious about, AI engines show us what people need to move forward. That shift changes how queries are written, how results are delivered and how content needs to be created.
In this article we’ll walk through the main types of queries that AI-engines pick up, why they differ from traditional search, and what you (as a marketer, SEO or content creator) should do about it.
The study of ChatGPT showed that nearly 80% of all conversations fall into three broad categories: “Practical Guidance,” “Seeking Information,” and “Writing”.
Meanwhile, newer engines like SearchGPT have surfaced queries that traditional search engines might never prioritize.
For SEO and content strategy, this means: the “query types” you optimize for are shifting. Not just keywords, but intent, formulation, and dialogue-driven requests.
The 6 core query types picked up by AI engines
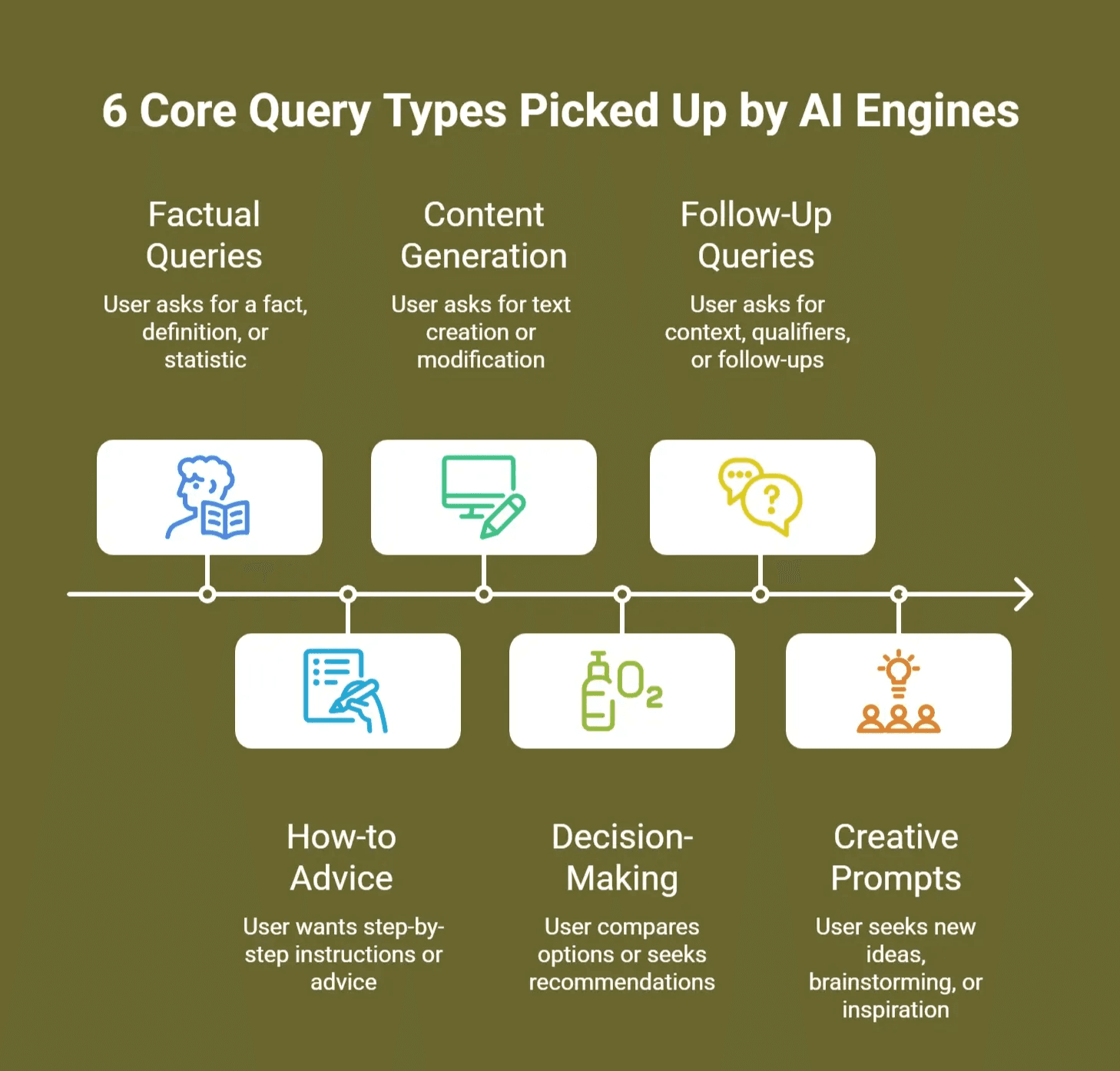
1. Seeking Information (Factual / Specific answer)
What it is: A user asks for a fact, definition, statistic, or a concise answer.
Example phrasing: “What is the capital of Finland?” “How many calories in a banana?”
Why AI picks these up: These are classic “information-seeking” queries. The ChatGPT usage data shows this is one of the major buckets.
AEO best practice: Give the AI answers it can lift cleanly. Keep definitions tight. Put the core fact in the first line. Add one or two supporting details. Use simple HTML structures like FAQs, tables, bullets. Label things clearly so the model can parse them.
2. Practical Guidance / “How-to” (Step-by-step / advice)
What it is: User wants a customized, actionable answer. “How do I…”, “What’s the best way to…”, “Guide me through…”
Example phrasing: “How do I create a content calendar for LinkedIn ads?” “Step by step: launch a B2B ABM campaign with LinkedIn”
Why AI picks these up: In the ChatGPT study, the “Practical Guidance” category (how-to advice, tutoring, creative ideation) remained ~29% of usage.
AEO best practice: Break your guidance into steps. Explain conditions. Add guardrails. Include short examples that show “when to use this versus when to avoid it.” Use headings the model can understand like “Step 1” or “If you have a small budget.”
3. Writing / Content Generation Assistance
What it is: The user asks for creation or modification of text (e.g., “Write a blog intro”, “Rewrite this”, “Generate captions”).
Example phrasing: “Write a compelling LinkedIn post about ABM targeting”, “Generate an outline for a blog on user onboarding software”
Why AI picks these up: The “Writing” category was a significant portion of work-related ChatGPT queries.
AEO best practice: Offer templates. Provide fill-in-the-blank frameworks. Include example outputs for different tones or use cases. Keep prompt-ready blocks in clean formatting so the model can reuse them.
4. Comparison / Evaluation / Decision-making
What it is: Queries where user is comparing options or making a decision. “Apollo vs Clearbit”, “Product Fruits vs WalkMe”, “best user onboarding tool under $500/mo”.
Example phrasing: “Apollo vs Amplemarket best for GTM teams”, “Which is better for product managers: Product Fruits or Appcues?”
Why AI picks these up: Marketers and users are shifting toward AI where they expect direct advice and comparisons. Also, the study of ChatGPT’s web-search behaviour shows deeper multi-page exploration.
AEO best practice: Use explicit comparison grids. Call out strengths, weaknesses, pricing, and ideal-fit scenarios. Label decision criteria clearly. Use verdict sections that summarise the winner for each type of user.
5. Long-Tail / Conversational / Follow-Up Queries
What it is: Queries that are more like dialogue, or follow-ups. For example: “What about if the budget is only 10k?” “And what if the target audience is mid-market firms?”
Example phrasing: “If we only have LinkedIn ads budget of $10K, what targeting should we use for ABM?”
Why AI picks these up: Approx 31% of ChatGPT prompts triggered external web search, and the average search length was ~5.5 words, longer than typical Google queries.
AEO best practice: Answer the main question, then add short follow-up sections titled “If you have a small budget” or “If your audience is mid-market” or “If you need this for Europe.” Use modifiers that match real conversational patterns.
6. Exploratory / Ideation / Creative Prompts
What it is: The user is looking for new ideas: “Give me 10 blog topic ideas for B2B ABM”, “Suggest innovative ways to engage C-suite on LinkedIn”, “Brainstorm features for a product launch”.
Why AI picks these up: One of the study’s insights was increased use of creative ideation in writing/Practical guidance.
AEO best practice: Create idea banks. Offer frameworks like “10 ways to brainstorm X” or “Prompts for Y.” Provide patterns the model can remix. Use lists that are long enough to feel rich but tight enough to avoid fluff.
Closing thoughts
The shift to AI-driven search and conversational query behaviour is a structural change in how people ask and how engines pick up queries. As content creators, SEOs and marketers we can no longer rely purely on traditional keyword buckets.
We must:
Think in terms of query-intents (information, decision, creation, comparison)
Design content that anticipates context and follow-up
Ensure our content is structured for AI-ingestion, not just human reading
Monitor how AI engines are picking up queries and citing content
By aligning with these changing query types, you’ll be well-positioned in a world where engines like SearchGPT and ChatGPT don’t just rank pages; they generate answers and cite your content.
FAQs
1. What types of queries do AI engines understand best?
AI engines understand natural language queries that include context, intent, and follow up detail. These typically fall into six categories: informational, how to, comparison, writing assistance, ideation, and decision making prompts.
2. How are AI queries different from Google keyword searches?
Google searches are often short and keyword driven, while AI queries tend to be longer, conversational, and goal oriented. Users ask AI for outcomes, not just information, which changes how content needs to be structured.
3. Why do AI engines pick up more long tail queries?
AI models interpret language naturally, so they recognize detailed prompts more effectively than traditional keyword based ranking systems. Long tail questions provide clearer intent, making it easier for AI to generate accurate answers.
4. How should I optimize my content for AI driven search?
Focus on direct answers, clear structure, context rich explanations, and question based headings. Include variations like “for beginners”, “with a small budget” or “for enterprise teams” to match conversational follow ups.
5. Are keywords still relevant in an AI first search world?
Keywords still matter, but intent matters more. Instead of optimizing for exact phrases, optimize for the underlying question and the user goal behind it.
6. Will AI engines replace traditional search?
AI engines are changing how users discover information, but traditional search will coexist. Over time, users will turn to AI for problem solving and decision making, and search for navigation, verification, and transactional needs.
Similar Blogs
Get found in AI search
Ready to start?








